The deployment progress of Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) is obtaining great momentum around the globe starting from 2020. According to Telecom Infra Project (TIP), the adoption of Open RAN solutions is accelerating with numerous Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) launching trials and commercial deployments to date as demonstrated in the following world map [1].
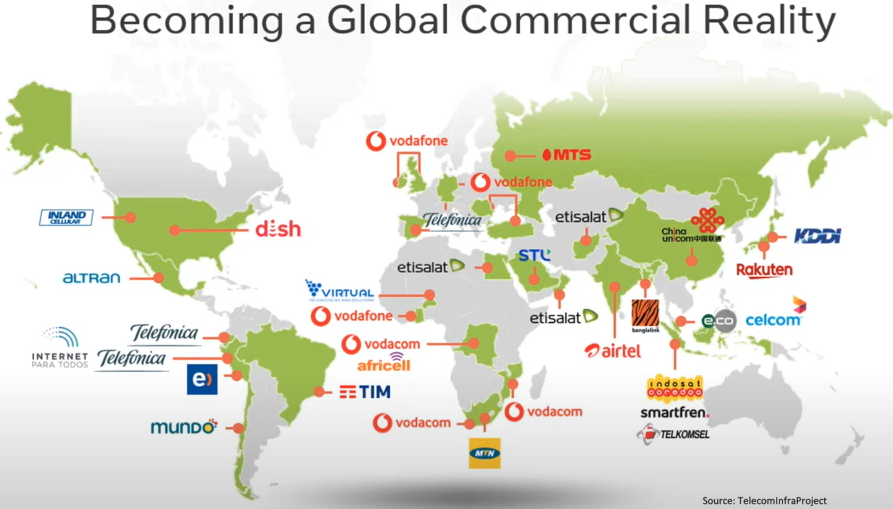
Source: TIP
Another research also expects the Open RAN ecosystem to reach a total market of US$30 billion in year 2030, climbing higher than Traditional RAN market which will be a total of US$20 billion for cellular network connectivity. It also projects the inflection point between Traditional RAN and Open RAN will happen during year 2028, whereby multi-vendor interoperable deployments in open interfaces will overtake proprietary vendor solution [2].
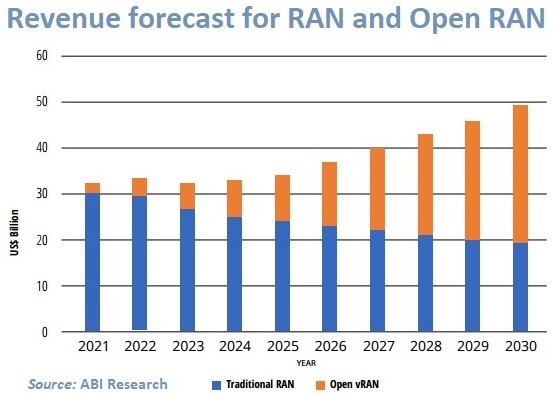
Source: ABI Research
Having seen the promising trend of Open RAN, MNOs need to maximize the benefits and savings in the same site deployment. Planning for Multi-Operator RAN (MORAN) sharing of infrastructure from Network Controller, Backhaul Transport, Base Transceiver Station (BTS) to Radio Unit or Distributed Antenna System (DAS) in utilizing the dedicated spectrum assigned to each sharing MNO become increasingly important. In the event of 5G upgrade to enable new use cases, more RAN equipment required by MNOs and Open RAN can be the viable option to further adding value in multi-operator sharing of site network infrastructure.
Less Equipment, Less Power Consumption
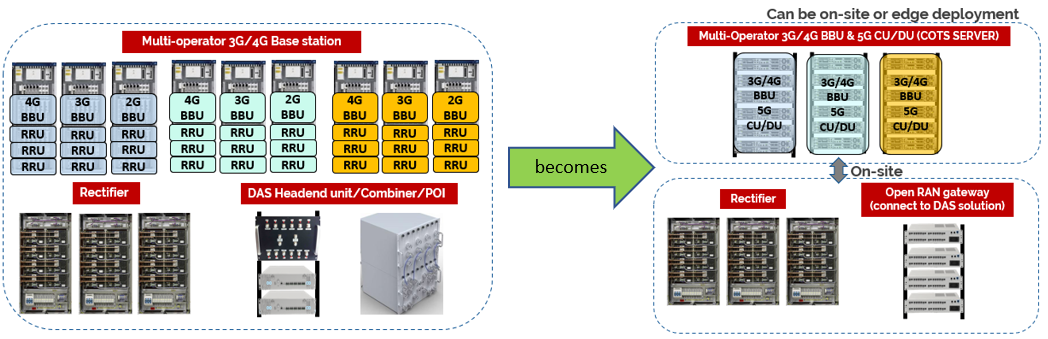
Traditionally, the BTS room is always packed with multi-system and multi-band RAN equipment in the multiple MNOs sharing scenario. Racks of hardware like Baseband Unit (BBU) and Remote Radio Unit (RRU), together with many rectifiers, headend unit and combiners are installed in the equipment area, whereby much power had been consumed. By considering Open RAN, the Centralized Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU) which running on common Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) server hardware can be deployed on-site with radio parts or located at the edge location thanks to flexible network architecture. The direct benefit that can be achieved is a lesser equipment footprint, and lowering down the energy power consumption. It will eventually lead to reduction of CAPEX and OPEX in multi-operator RAN sharing deployment.
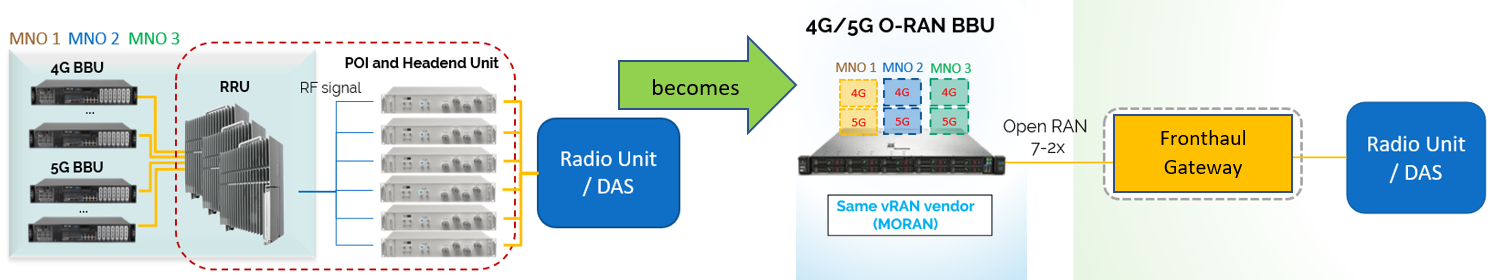
Streamlined with Open Fronthaul Split 7-2
In Open RAN, an open fronthaul gateway supporting Option 7-2 split defined in O-RAN specification would become an emerging trend when increasing the number of proven trials taking place in the markets, especially from 2021 and beyond. Adding light to this, with disaggregation of hardware and software enabled in Open RAN, the conventional BBU hardware of each MNO can be transformed into virtualized BBU in a lean COTS server. As a result, the overall architecture can be streamlined for multi-operator sharing in Open RAN configuration.
Open RAN is designed to take one step forward in the acceleration of 5G upgrade and realization of use cases. The evolving technology will definitely add value in multi-operator sharing, and it is actually bringing benefits to any type of deployment, be it macro or indoor network. We shall witness more deployment cases of Open RAN to come in the near future.
Sources:
[1] “TIP OpenRAN Project Group is Streamlined to Accelerate Development and Deployments”, TIP, published October 2020, https://telecominfraproject.com/tip-openran-project-group-is-streamlined-to-accelerate-development-and-deployments/
[2] “Open RAN: Market Reality and Misconceptions”, ABI Research, published June 2020, https://go.abiresearch.com/lp-open-ran-market-reality-and-misconceptions

